
Posted by:
Admin
Date:
January 27, 2026
Category:
Landlord Tax Returns Made Simple: A Step-by-Step Guide
Are you a landlord having issues with your tax returns? Do you find self-assessment to be hectic? Rental property can be a very lucrative asset. But being a landlord comes with certain responsibilities. For instance, timely HMRC landlord tax returns are a must. However, taxes can be confusing, therefore, knowing how to file your landlord self-assessment tax return is very important. As a landlord in the UK, you must declare your income from rent to HMRC and pay the following taxes.
- Income tax on rental profits.
- Stamp duty land tax on the purchase of property.
- Capital gains tax on the sale of an asset.
- Voluntary Class 2 national insurance if being a landlord is your main occupation.
For many landlords, tax matters can be difficult. With a step-by-step guide, landlord taxation can be easily managed.
This guide will explain all you need to know about landlord tax returns. We will cover everything from rental income, allowable expenses, deadlines and much more to make the process of filing returns simpler. We will clear the difference between the landlord self-assessment tax return and HMRC landlord tax return, so that all things are made clear for you to understand. Let us begin.
At a Glance: Landlord Tax Returns UK (Self Assessment)
This step-by-step guide explains how UK landlords file a landlord self-assessment tax return. It covers:
Who it’s for: UK landlords who earn more than £1,000 a year from renting out property (the £1,000 is the property allowance).
What you’ll achieve: Learn if you should contact HMRC (£1,000 to £2,500) or file a Self Assessment tax return (over £2,500 after allowable expenses / over £10,000 before allowable expenses), then follow the steps to file on time and avoid penalties.
- When a landlord must file a tax return (including the £1,000 property allowance).
- How to register for Self Assessment and get a UTR.
- What rental income to declare to HMRC?
- Which allowable expenses can be claimed?
- How to calculate rental profits and tax.
- Key deadlines for paper and online returns.
- Digital tax returns (Making Tax Digital) and who they apply to.
- Common mistakes that lead to penalties.
What Is a Landlord Tax Return?
The landlord tax return is the process through which landlords file self-assessment reports about their rental income and expenses to HMRC. This report is submitted to HMRC through the main SA100 form and the supplementary SA105 pages for property income. In case you file online, HMRC will calculate the tax. For paper filing you or an accountant will have to work out the tax. The landlord has to file that tax within the time limit. Failure to do so may result in penalties.
This process ensures that:
- All income from your rental properties is declared.
- Deduct expenses to lessen your tax.
- You pay the right amount of tax.
- Make sure that your tax returns are in compliance with HMRC regulations.
Landlords have to report their income and expenses manually. As part of this process, you complete a landlord self-assessment tax return.
To learn more about taxation on rental income, check out our guide on paying tax on rental income.
Who Needs to File a Landlord Self-Assessment Tax Return?
You are eligible to file landlord self-assessment tax return if your rental income exceeds £1,000. The first £1,000 of your rental income is tax-free. This is the tax-free allowance. If your income is anywhere between £1,000 to £2,500, you should report to HMRC. If it’s more than £2,500, you must report landlord tax return on a self-assessment tax return after allowable expenses and £10,000 before allowable expenses.
Other than basic limits, you are eligible for a landlord taxation return if any of the following conditions are met:
- You own furnished holiday lettings (FHL) or overseas property.
- You jointly own a property and receive rent from it.
- The total income from all your rental sources exceeds the personal allowance.
- You have sold a rental asset.
- HMRC has issued a notice to file a return.
Even if your income is below the allowance limit, it is good to file a return to claim tax relief.
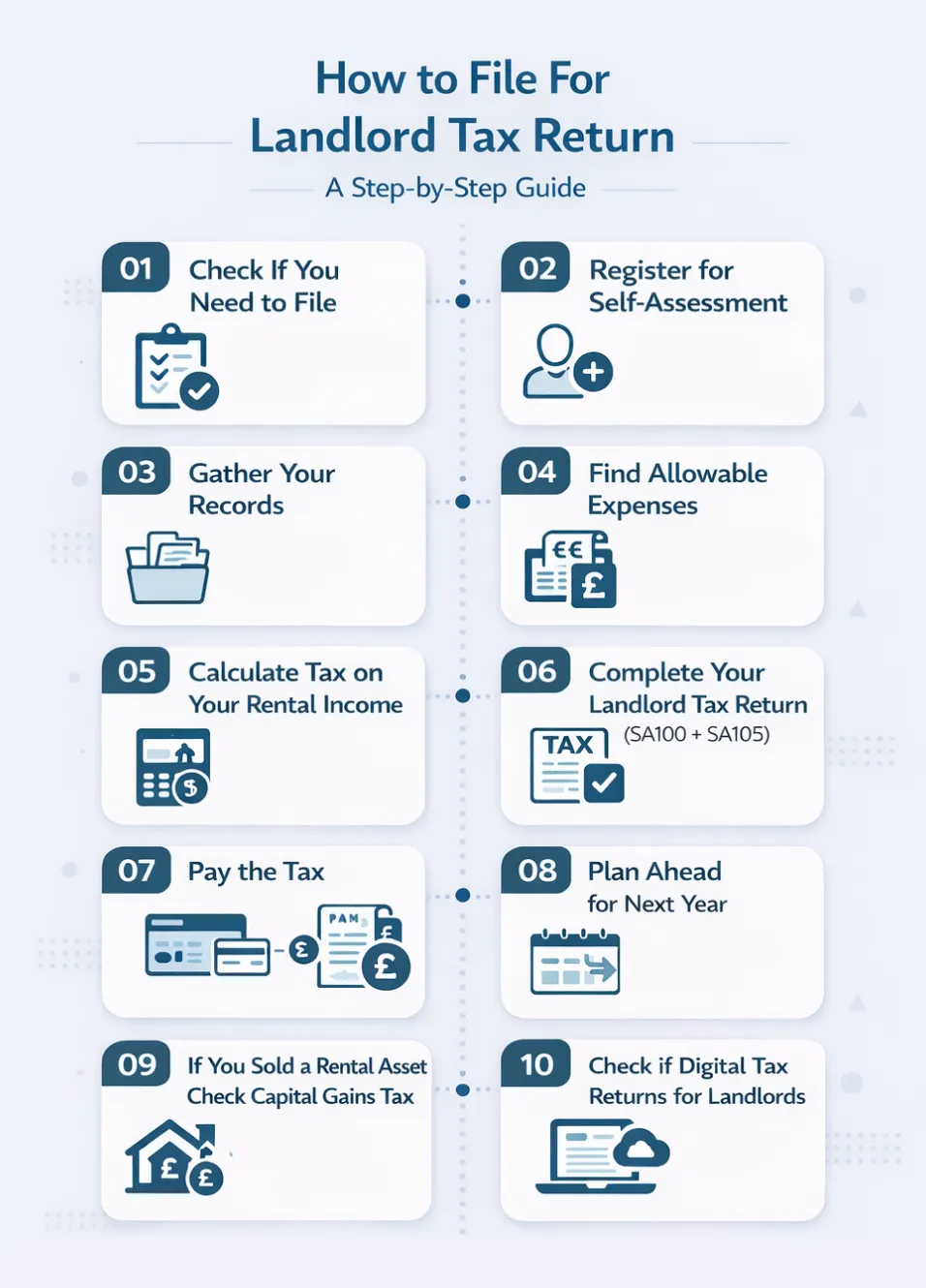
How to File For Landlord Tax Return: A Step-by-Step Guide
Now we will go through each step of the process of filling out the landlord self-assessment tax return. Before laying out the process, we should understand what a landlord tax return is and what is the eligibility criteria for it.
Step 1: Check If You Need to File
Before even starting to file, you must make sure that you are eligible to file for the tax return. The conditions for filing have already been provided. Work out your income and expenses to see if it is above the taxation threshold. If your income from rental property is above £1,000, then you may need to register for self-assessment.
Step 2: Register for Self-Assessment
Before filing for your first landlord tax return, you need to register with HMRC. Registration can be done online or via form SA1. For landlords, you have to fill form SA-105. This is a document that discloses your earnings from rent. If you are filling online you may not have to fill SA-105.
Here is how you register online:
- Visit the HMRC online registration portal.
- Complete form SA1 (if you already have a tax record), or the self‑employed registration if applicable.
- You need to enter your National Insurance number, address, and letting start date.
- Receive your Unique Taxpayer Reference (UTR).
This UTR must be kept safe. It is needed every time you complete an HMRC landlord tax return.
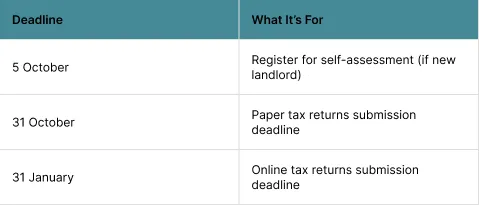
Important Deadlines
Here are some important deadlines. Missing these deadlines may result in penalties and interest.
Step 3: Gather Your Records
The most important thing in maintaining a smooth tax return is keeping clean records. Records include:
- Rental income received.
- Allowable expenses paid.
- Mortgage interest statements.
- Receipts for repairs and maintenance.
- Tenancy agreements and deposits.
HMRC requires that you keep these records for at least five years after the 31 January filing deadline for the relevant tax year.
Step 4: Find Allowable Expenses
Allowable expenses are the expenses you can deduct from your income before calculating your taxable profit.
Quick rule: repairs and maintenance are usually allowable, but improvements (upgrades that add value) are not treated the same way.
There is a wide range of costs you can deduct before calculating tax.
Common Allowable Expenses:
- Letting agent fees.
- Property insurance.
- Maintenance and repairs (not improvements).
- Utility bills (if the landlord pays).
- Council tax (if landlord is responsible).
- Legal and accounting fees.
- Advertising for tenants.
- Inventory and tenancy setup costs.
All these expenses must be deducted from your net income before calculating HMRC landlord tax return.
Reminder:
Mortgage interest is no longer deducted from rental income. You receive a 20% tax credit based on your finance costs. This change can change your tax position, at this rate, even some basic taxpayers can be pushed into a higher-rate taxpayer category.
The impact is strongest on higher-rate taxpayers. As the 20% credit increases their tax liability.
Step 5: Calculate Tax on Your Rental Income
Your taxable profit is calculated as:
Net rental income = Rental income – Allowable expenses
For instance,
If your rental income = £24,000 per year
Your allowable expenses = £6,000
Your net rental income = £24,000-£6,000 = £18,000.
This is the figure that will be taxed through your landlord self-assessment tax return.
If you own multiple properties, you must combine all rental income and expenses to calculate total profit. HMRC treats your rental business as a single entity even if you have many properties.
Step 6: Complete Your Landlord Tax Return (SA100 + SA105)
Use form SA100, with supplementary pages SA105 for property income.
You’ll need to:
- Enter rental income.
- Deduct allowable expenses.
- Include mortgage interest as a tax credit.
- Report other property income (holiday lets, overseas rentals).
- Online submission is recommended. It’s quicker, reduces errors, and gives instant confirmation.
Step 7: Pay the Tax
After submitting your landlord self-assessment tax return, HMRC calculates your tax liability. Payment options include:
- Bank transfer.
- Direct debit.
- Debit/credit card.
If your tax bill exceeds £1,000, HMRC may require payments on account, which are advance payments toward next year’s tax. These are due:
- 31 January – First payment.
- 31 July – Second payment.
If you cannot pay in full, you can request a payment plan. HMRC allows for that.
Step 8: Plan Ahead for Next Year
Effective tax planning allows landlords to:
- Keep accurate records.
- Utilise allowable expenses.
- Plan for Capital Gains Tax on future property sales.
- Consider alternative ownership structures, such as limited companies, for tax efficiency.
Keeping on top of these steps ensures your HMRC landlord tax return is straightforward in subsequent years.
To get more planning and tips for saving on tax, check out our top tax saving tips.
Step 9: If You Sold a Rental Asset Check Capital Gains Tax
Capital Gains Tax or CGT is applied when you sell a rental asset. It is the tax on gains made from the proceeds. It is calculated as:
Gains = Sales price – purchase price – costs
Note: “Costs” can include certain buying/selling fees and some improvement costs, and special rules/reliefs can apply. Always check what HMRC treats as allowable for your situation.
The amount of tax depends on a number of factors such as the gains made, the type of asset and whether you are a basic taxpayer or a higher taxpayer.
Capital gains tax does not apply if the asset in question was your main home. There are also letting reliefs in limited cases.
Step 10: Check if Digital Tax Returns for Landlords Apply
HMRC requires landlords with income above £50,000 to use digital records and submit updates quarterly. This has been in effect since 6 April 2026. By 6 April 2027, the threshold will lower to £30,000. Benefits of digital tax returns for landlords include:
- Reduced risk of errors
- Easier end-of-year filing
- Less paperwork and faster updates
- Investing in compatible software early can save significant time
Some Errors to Avoid
Even with proper guide taxes can be tricky. There are some pitfalls you need to be aware of as a landlord, when filling landlord tax returns.
- Avoid last-minute filing. Delays can be messy and deadlines are subject to change.
- Mixing of incomes. Don’t mix personal and rental expenses. A list of rental expenses has been provided in this guide.
- Non-declaration of income. Make sure that all income, including deposits and overseas assets are declared.
- Loss of records. Loss of records can lead to penalties and extra interest. Make sure to keep digital and physical copies of all records.
- Not getting an advisor. An advisor can help a lot when dealing with taxation. Proper calculation and accounting of assets are key for stable finances. Getting expert help is always the right move.

Conclusion
So there you have it. A comprehensive guide for landlords on tax returns. Taxation is often seen as hectic. It doesn’t have to be provided you:
- Maintain accurate records
- Don’t mix your expenses
- Do the right calculations
- Stay ahead of deadlines
By doing these steps, you can save money and make the process smoother for you.
Getting professional advice can be of great value in working multiple properties and complex tax situations. That’s where we come in, at Sterling Cooper Consultants we can help you optimise your HMRC landlord tax return. No more missed deadlines or wrong calculations. With us, your taxes are done accurately and timely. Contact us now to start a stress-free financial journey today.
Take control of your landlord tax return today.
FAQs
Recent Posts


