
Posted by:
Admin
Date:
January 2, 2026
Category:
blogs
The Ultimate VAT Exemption Guide
Are you confused about VAT categories and not so sure about which one your business falls in? We have got you covered. Knowing how VAT exemption works is empirical for people and businesses working in the UK.VAT can be a complex area, mainly when certain goods or services do not carry VAT at all. If you fall into a category for VAT exemption, you could legally avoid paying VAT. It can help you save a large amount of money. Our guide will explain all you need to know about the topic.
What is VAT Exemption?
It means a good, service, or activity is totally free from VAT. Unlike zero-rated goods, exempt items do not carry VAT. Same way the setups that sell them cannot reclaim VAT on related purchases.This makes VAT exemption different from zero rating. Even though both result in no VAT charged to the final consumer.VAT Exemption vs. Zero-Rating
Even though both can result in no VAT charged to the customer, the business impact is different. Zero-rated supplies are still taxable supplies at 0%. Exempt supplies are not treated the same way.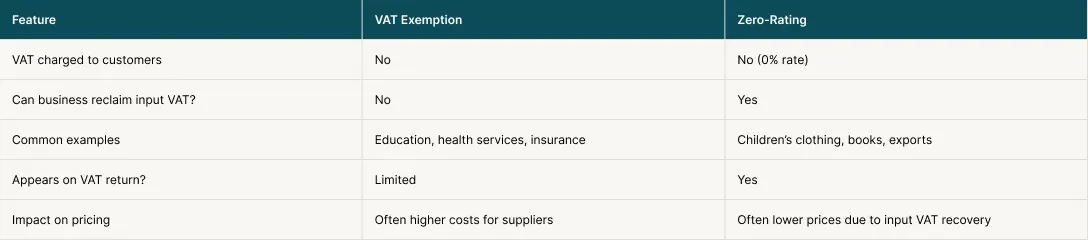
Simplify your taxes with expert planning, VAT returns & corporation tax services in the UK.
What Are the Common Categories for VAT Exemption?
Exempt supplies are mostly linked to essential services where VAT would make access harder. That is why many exemptions cover education, health, and other areas of welfare.Still, these rules can have conditions, and not every service in these sectors is exempt. Below are common areas that often fall under exemption in the UK.1. Education
Teaching and training from approved schools and tutors are usually exempt. This helps learning stay more affordable for students. Many private lessons also fall under VAT exemption.2. Health
Medical care from doctors, nurses and clinics is often exempt. This includes treatment, tests and hospital care. The rule helps keep basic health services easier to access.3. Charity Fundraising
It may get VAT exemption for some events. The fundraising event must raise money for their main work. This saving helps charities spend more on their cause.4. Financial Services
Banking, loans, credit, and insurance services often qualify. These services are common in daily life, so exemption keeps costs low.5. Gambling
Betting, lotteries and gaming are exempt from VAT. These setups follow separate tax rules set by the government.6. Land and Property
Renting a home or dealing with some land agreements can be exempt. Most residential property rentals fall into this group.7. Burial
Funeral services, burial plots and cremations are exempt. This reduces the financial burden during difficult times.The UK government has shared the VAT rates on different goods and services which also shows the VAT exempt items.Who is Eligible for VAT Exemption?
Eligibility depends on what is being supplied and who is receiving it. Some exemptions are based on the type of service, such as healthcare. Others depend on the buyer, such as goods for disabled people.A business also needs to understand how exemption affects its VAT registration position. Because exemption does not always remove duties.Here is a detailed account of people, businesses and services eligible for VAT exemption:1. Individuals
Some VAT exemptions are based on the personal situation of the buyer. These rules are mainly designed to support daily living, health needs, and mobility. In most cases, the exemption applies only when the goods are for personal use and meet strict conditions.i. Elderly People
Many aids made for older people qualify for VAT exemption. This includes equipment that helps with daily living.ii. Disabled People
Disabled people can buy medical and mobility products without VAT. The rule supports independence and comfort.iii. Tourists
Some tourists may qualify for VAT refunds, depending on current UK rules. This usually applies to goods taken out of the country.2. Businesses
Many VAT exemptions depend on the nature of the service being supplied. These exemptions are common in sectors that provide essential or public interest services. Businesses must still check how exemption affects VAT registration and input VAT recovery.i. Small Setups and Startups
Some small firms provide exempt services by nature. They do not charge VAT on these supplies.ii. Charities
These may get exemption for fundraising and welfare work. It lets them use more of their income on community needs.iii. Healthcare Providers
Doctors, clinics, dentists and therapists often give exempt services.iv. Educational Institutions
Schools, colleges and training centres often fall under exemption. Their main teaching work qualifies for relief.v. Financial Service Providers
In this case, banks, insurers and mortgage firms offer exempt services that follow strict rules.vi. Mixed Supply Setups
Some businesses sell both VAT exemption products and taxable goods. These firms must handle VAT carefully and follow partial exemption rules.vii. Exports
Some global services are not charged VAT at all. They may fall outside UK VAT rules.viii. Land and Property
Residential rents and some land services qualify for exemption.3. Products & Items
Certain goods qualify for VAT exemption because of how they are used. Most of these items support medical care, disability needs, or essential living requirements. Eligibility often depends on who the item is for and how it will be used.i. Medical Equipment
Wheelchairs, hospital beds and care items are VAT exempt goods. They support basic medical needs.ii. Mobility Aids
Stairlifts, scooters and walking aids often qualify for exemption products. This is for eligible buyers.iii. Children’s Clothing and Footwear
These items do not have VAT, but they are zero-rated rather than exempt.iv. Books
Printed books and newspapers are also zero-rated. They remain VAT free for buyers.v. Prescription Medicines
These are also VAT exempt goods. It makes the vital treatment affordable.vi. Energy-saving Products
Some energy-saving items may qualify for VAT relief under current rules.vii. Specific Disability Products
Adapted vehicles, assistive devices and similar items can be bought without VAT.How to Claim or Apply VAT Exemption?
The process usually comes down to proof and correct paperwork. Suppliers need to confirm eligibility before selling without VAT. Buyers need to provide the right details. When this is done the proper way it stays simple. Ignoring it creates problems later. Here are the key steps to follow while applying for exemption:- Check That the Product Qualifies
- Declare Your Eligibility
- Complete a VAT Relief Form
- For Online Purchases
- For In-Store or Telephone Purchases
- For Charities
How VAT Exemption Works?
Given below is how it actually works in different scenarios:- No Output VAT: Businesses do not charge VAT on exempt supplies.
- No Input VAT Reclaim: They cannot recover VAT on related purchases. It increases overall business costs.
- Partial Exemption: For those selling both exempt and taxable goods, they must calculate how much input VAT they are allowed to reclaim. This requires careful record keeping.
What Are the Pros and Cons of VAT Exemptions?
Lets walk through some general pros and cons of VAT Exemptions:Pros of VAT Exemption
- No VAT is added to the final price for customers
- Helps keep essential services more affordable
- Reduces tax burden for certain activities
- Supports access to health, education, and welfare services
- Can make pricing clearer for customers
- Avoids the need to charge and collect VAT on exempt supplies
- Useful for businesses focused on non-commercial or social goals
Cons of VAT Exemption
- Input VAT on purchases cannot be reclaimed
- Business running costs can increase
- Less flexibility in tax planning
- Can reduce profit margins for cost-heavy businesses
- Mixed activities create extra complexity
- Requires careful record keeping to avoid mistakes
- Confusion between exempt and zero-rated supplies is common
- May limit growth options if VAT recovery becomes important

What Are the Common VAT Mistakes?
VAT errors usually happen due to confusion, rushed invoicing, or weak records. Most mistakes are avoided once the VAT status is clear and the team follows one consistent process.Here are a few mistakes that are commonly made and should be avoided:- VAT on Exempt Services: Many firms add VAT by accident. This must be corrected.
- Reclaiming VAT on Exempt Supplies: Input VAT on exempt sales cannot be reclaimed. Incorrect claims may cause penalties.
- Confusing Exempt with Zero-Rated Supplies: These two categories work in different ways. Mixing them causes VAT errors.
- Incorrect Invoicing: Invoices must show clearly that the supply is exempt.
- Mixing Exempt and Taxable Items: Poor separation leads to wrong VAT returns.
- Exceeding the Threshold: Some activities may force the business to register even if many sales are exempt.
- Claiming Wrong Input VAT: Partially exempt firms often make mistakes in this area.
- Poor Record-Keeping: Weak records make VAT checks harder and risk penalties.
What Are the Record-Keeping Tips?
Knowing the category early saves time later. It also reduces panic during VAT deadlines. Here are a few tips to be kept in mind for avoiding any confusions about your status:- Know Your VAT Status: Know if you are exempt, partially exempt or taxable. This guides all VAT actions.
- Keep Thorough Records: Store all invoices, forms and receipts. Good records protect you in case of checks.
- Organise Documents Clearly: Separate exempt and taxable items. This keeps things simple and clean.
- Separate Personal Expenses: Clear separation prevents confusion during VAT reviews.
- Retain Records: Keep your records for at least six years.
- Include a Clear Note: Write “VAT exempt” or a similar note. This avoids confusion for customers and HMRC.
Conclusion
Being fully aware of VAT exemption is always needed. It helps to reduce the costs. Firms can then operate in an efficient way. For new business owners, the safest approach is to set up clean systems early. Even simple steps like correct invoices, neat records, and clear separation may prevent future stress. For established ones, reviewing VAT treatment once a year is a smart move. Services change. Supplies change. And VAT rules also get updated.Sterling Cooper Consultants guide you on how VAT works. We will let you know who qualifies, and how to apply. In this way we ensure you stay compliant and avoid mistakes.For further guidance about managing your VAT, reach out to our experts.Know your VAT.
Contact us today for tailored VAT support and professional accounting advice.
FAQs
The VAT exemption rule means some goods and services do not have VAT added at all. These supplies are outside the VAT system, so businesses do not charge VAT and cannot reclaim on related costs. Examples include education, healthcare, insurance, charity fundraising and some financial services.
You can remove the 20 percent VAT only if the item is VAT exempt or zero rated. If the supply qualifies, the invoice must show “VAT exempt” or “Zero rated”. You cannot exclude VAT from standard-rated items unless the law allows it.
In most cases, there is no official VAT exemption certificate. Instead, buyers complete a simple VAT relief declaration form provided by the supplier. Charities may give a certificate confirming they qualify for VAT relief on certain purchases.
For VAT-exempt items, no VAT is added, so the computation is simply the net price. Businesses with mixed supplies must separate exempt and taxable sales and follow HMRC’s partial exemption rules for input VAT.
As of January 1, 2021, the UK government discontinued the VAT refund scheme for tourists. For many visitors, this decision ended an era of cost-effective shopping in Britain.
Recent Posts


